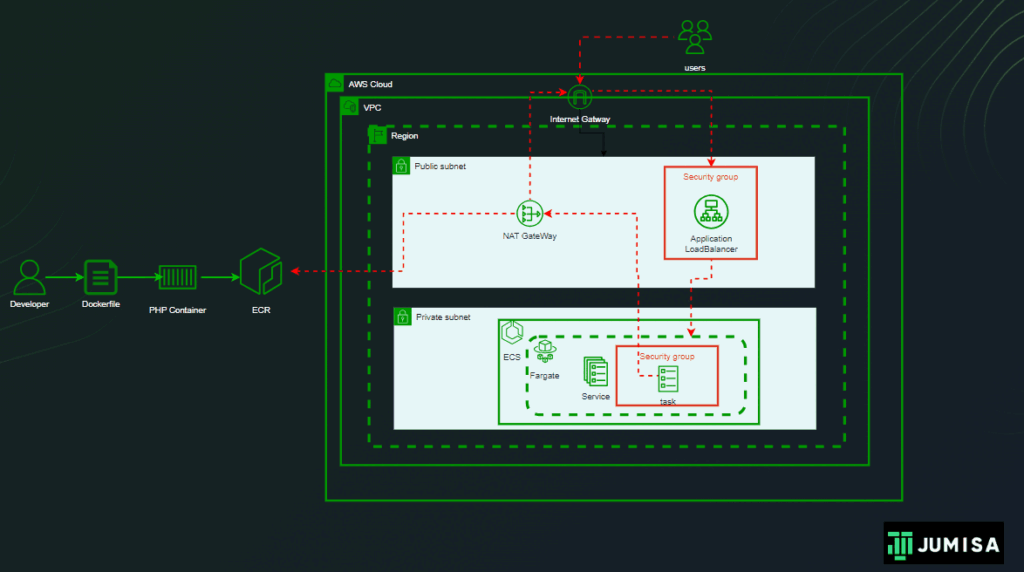
What is Smooth Cloud Migration?
Smooth Cloud Migration refers to the process of moving an organization’s digital assets, services, databases, IT resources, and applications from on-premises data centers to a cloud environment in a seamless, efficient, and minimally disruptive manner.
Smooth Cloud Migration: Transition to AWS
Migrating to Amazon Web Services (AWS) can offer numerous benefits, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, achieving a smooth transition requires careful planning and execution.
Here is a step-by-step guide to ensure a seamless migration to AWS.
1. Assessment and Planning
a. Assess Current Environment:
- Inventory Applications and Data: Catalog all applications, databases, and services currently in use.
- Evaluate Dependencies: Identify dependencies between applications and services.
- Performance Requirements: Assess the performance and capacity requirements of each application.
b. Define Migration Goals:
- Business Objectives: Define the business outcomes you aim to achieve, such as cost reduction, improved performance, or enhanced scalability.
- Success Criteria: Establish metrics for success, such as downtime tolerance, performance benchmarks, and user satisfaction.
c. Create a Migration Plan:
- Timeline: Develop a realistic timeline with milestones.
- Resources: Allocate the necessary resources, including personnel, budget, and tools.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies.
2. Choosing the Right AWS Services
a. Compute:
- EC2: Use Amazon EC2 for scalable computing capacity.
- Lambda: Utilize AWS Lambda for serverless computing where appropriate.
b. Storage:
- S3: Use Amazon S3 for scalable object storage.
- EBS: Use Amazon EBS for block storage needed by EC2 instances.
c. Database:
- RDS: Use Amazon RDS for managed relational databases.
- DynamoDB: Use DynamoDB for NoSQL databases.
3. Data Migration
a. Transfer Methods:
- AWS Data Migration Service (DMS): Use AWS DMS to migrate databases to AWS with minimal downtime.
- AWS Snowball: Use AWS Snowball for transferring large datasets physically.
b. Data Validation:
- Consistency Checks: Ensure data integrity and consistency before and after the migration.
- Security: Implement encryption and access controls to secure data during transfer.
4. Application Migration Strategies
a. Rehosting (Lift and Shift):
- Direct Move: Move applications to AWS without making changes to the underlying architecture.
- Automation: Use AWS Server Migration Service (SMS) to automate the migration of on-premises servers to AWS.
b. Replatforming:
- Optimization: Make limited changes to optimize applications for the AWS environment.
- Containerization: Consider using Docker and Amazon ECS/EKS for containerized applications.
c. Refactoring:
- Cloud-Native: Re-architect applications to fully leverage AWS services and features.
- Microservices: Break down monolithic applications into microservices using AWS Lambda and API Gateway.
5. Testing and Validation
a. Pre-Migration Testing:
- Test Environment: Set up a testing environment on AWS to validate the migration process.
- Performance Testing: Conduct performance and load testing to ensure applications meet requirements.
b. Post-Migration Testing:
- Functional Testing: Ensure all applications and services are functioning correctly post-migration.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Validate the migration with end-users to ensure it meets their needs.
6. Security and Compliance
a. Security Best Practices:
- IAM: Implement AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) for secure access control.
- Encryption: Use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to manage encryption keys.
b. Compliance:
- Audit and Logging: Use AWS CloudTrail and AWS Config for auditing and monitoring compliance.
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensure your migration meets relevant regulatory and industry standards.
7. Training and Support
a. Training Programs:
- AWS Training: Provide AWS training and certification for IT staff.
- Documentation: Develop comprehensive documentation for end-users and administrators.
b. Support Structures:
- AWS Support Plans: Choose an appropriate AWS Support Plan for your needs.
- Internal Support: Establish internal support teams to handle issues and provide assistance.
8. Monitoring and Optimization
a. Performance Monitoring:
- AWS CloudWatch: Use CloudWatch to monitor application performance and resource utilization.
- Alerts: Set up alerts for critical performance metrics.
b. Cost Optimization:
- Cost Management Tools: Use AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets to track and manage costs.
- Resource Optimization: Regularly review and optimize resource usage to minimize costs.
By following these steps, you can ensure a smooth and efficient migration to AWS, minimizing disruptions and maximizing the benefits of cloud computing.